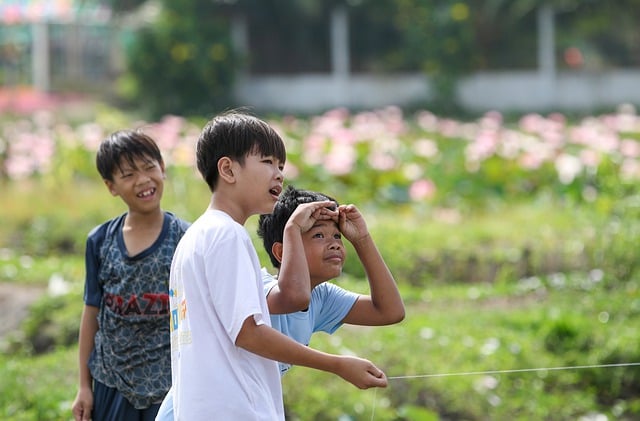
The article explores the significant relationship between social connections and longevity, highlighting that individuals with stronger social relationships have a 50% higher likelihood of survival compared to those with weaker ties. This study emphasizes the importance of social networks in promoting health and well-being, suggesting that fostering strong relationships can be a crucial factor in enhancing life expectancy. The findings encourage further investigation into how social interactions contribute to overall health outcomes, potentially informing public health strategies aimed at improving community support systems.
Editor’s Note: The importance of social interaction for longevity underscores a fundamental aspect of what it means to be human: our inherent need for connection. In the West, particularly during the isolating times of the COVID-19 pandemic, many individuals found themselves distanced from family and friends, leading to profound emotional and physical consequences. This isolation not only diminishes quality of life but also significantly impacts health outcomes, as loneliness can exacerbate stress, depression, and various chronic illnesses.
Spiritual traditions often emphasize community and relationships as vital for personal growth and healing; for instance, many indigenous cultures view communal bonds as essential to individual well-being. Recognizing that our social networks are integral to our survival invites a deeper understanding of the human experience—reminding us that fostering connections is not merely a social nicety but a crucial component of a healthy, fulfilling life. As we navigate an increasingly fragmented world, prioritizing relationships can serve as a powerful antidote to isolation, enhancing both our longevity and the richness of our lives.
Read Original Article
Read Online
Click the button below if you wish to read the article on the website where it was originally published.
Read Offline
Click the button below if you wish to read the article offline